Blog Post
Common Injuries That Can Be Taken Care of with EMCARE's First Aid Training

We are going to help you learn the ins and outs of first aid training, which we make available to you in the form of 4 emergency and medical courses: Basic First Aid, First Aid Level 1, First Aid Level 2 and First Aid Level 3. In these courses, EMCARE professionals teach you how to handle any accident confidently and ethically. Read this article if you're interested in learning more about the types of injuries you will have to treat.
Be Prepared For Everyday Accidents and Dangers
In life, it is better to be prepared for the worst rather than expecting the best. You never know what dangers could be lurking around the corner. Accidents happen every minute, and any emergency response professional within the medical industry will tell you that it only takes a moment to separate life from death. This is precisely why it is so important to ensure that you have the knowledge and necessary skill level to handle whatever situation presents itself.
By taking a first aid course, you could quite literally save somebody's life one day. At EMCARE, we offer first aid training in multiple branches all over South Africa. These classes include everything from emergency scene management, CPR, burns, fractures, wounds, legal implications, ethics and equipment. But in order to get you familiar with the course material, we want to offer you a comprehensive, theoretical look into the types of injuries that are going to require your attention.
Burns
A burn is a type of tissue damage that comes from direct contact between the skin and any thermal heat, such as steam, an open flame, chemicals, friction, sun-damage, electricity, hot liquids, radiation or hot metal. This is a very common accident that can happen to anyone both professionally and casually. For example, burns can happen at home while manning the braai, preparing a bonfire, or even straightening your hair. Professionally, it is not uncommon to see serious burn victims seeking treatment because of an accident in a restaurant kitchen - in the case of a chef - or after the extinguishment of a domestic fire - in the case of firefighters.
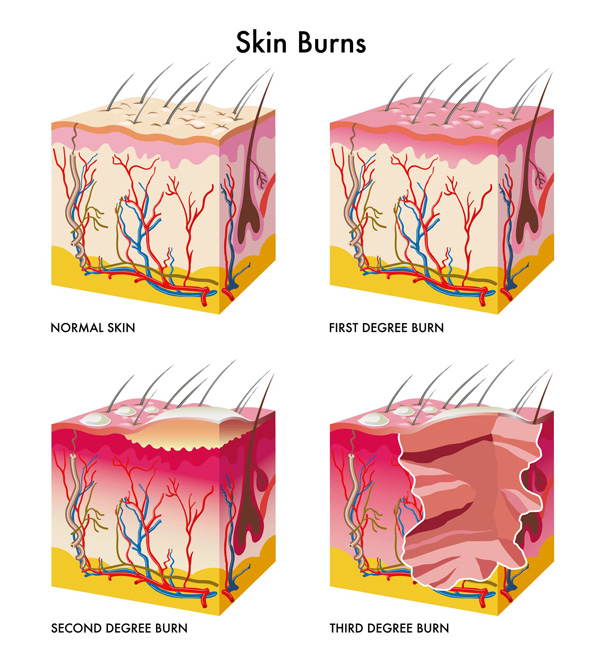
There Are 3 types Of Burns:
- First-degree burns
These burns are the least severe burns. They can cause red, raised skin and a sore-to-touch epidermis. These burns are painful but manageable for any first aid responder. - Second-degree burns
These burns are more serious. They affect the upper layer of the skin (the epidermis) and the layer below it (the dermis). In these cases, victims may find themselves in danger of blisters, red, raised skin and painful swelling. - Third-degree burns
These burns affect the epidermis, dermis and the deeper tissue. They are incredibly dangerous and often very sore. They tend to numb, blacken or charr the skin until it becomes black or even white. - Fourth-degree burns
These burns can affect your muscles, bones and nerve-endings. It is not uncommon to find that people who experience fourth degree burns lose feeling in the affected areas. These burns put a victim at risk of having their fat, skin and muscles destroyed.
Treating Burns
When treating burns, there are a variety of hidden factors which can exacerbate a bad situation. Many people go into shock if their burns are severe enough, and often people make the mistake of placing a bad burn in cold water - which can cause a drop in body temperature and resultant hypothermia - or treating an unclean wound. With first aid training, you'll learn how to treat a burn by implementing the following steps:
- Removing the person from the danger or source of heat.
- Discerning the gravity of the situation and whether the authorities need to be alerted.
- Identifying the degree of the burn.
- Keeping the burn or wound clean.
- Wrapping the affected area in gauze.
- Preventing additional complications such as hypothermia, tetanus, sepsis, extreme blood loss or unconsciousness
- Managing shock, dizziness and fainting.
- Doing mouth-to-mouth resuscitation in the case of fainting.
Wounds and Bleeding

There are two types of wounds. The first category pertains to wounds caused by blunt force trauma. The second type of wound pertains to wounds caused by penetration. Wounds are classified as a breakage or separation of the skin, which leads to exposed body tissue and the damage of the epidermis and or dermis.
Wounds Caused By Penetration
- Thermal, chemical or electric burns
- Surgical incisions
- High velocity debris or objects that hit the body
- Bites
- Stings
- Gunshot wounds
- Puncture wounds
- Cuts
- Scrapes
Wounds Caused By Blunt Force Trauma
- Lacerations
- Tears in the skin
- Abrasions
Other types of closed, internal wounds and bleeds are generally more serious and students will be educated on discerning whether the victim's symptoms are grave enough to alert an ambulance or medical authorities. For example, major types of closed wounds include contusions, crushes, blisters, hematomas and seromas. Students working with EMCARE first aid training will learn to treat external wounds rather than internal wounds, which should be handled by doctors. Understanding the different types of wounds will help you to identify whether further medical treatment and stitches are necessary.
Moreover, attaining first aid training will help you to treat less severe wounds while preventing additional complications like infection. Wounds and bleeding can be caused by significant force, such as from a gunshot, animal bites, sharp objects, scratches, fights, falls or even attacks. Open wounds can result in swelling, bleeding and pain. In the case of a serious wound, it is always best to minimise blood loss, clean the wound surgically and treat any fever, fainting or vomiting which might follow.
Treating Wounds With First Aid Training

There are a variety of steps and risk management techniques that can be taught through first aid training in the case of wounds and bleeding. EMCARE teaches first aid students how to stop the bleeding, clean the wound and protect the area. Read the steps below to see the type of skills you will learn during first aid training:
-
Stop the Bleeding
Students will learn how to apply direct pressure to a cut or wound, and use gauze, tissue or cloth to prevent further blood loss. They will learn also how to correctly sanitise the wound and minimise any pain caused. They will be taught how to apply a tourniquet in the case of serious cuts or wounds. -
Clean the Wound
Students will be taught how to correctly sanitise themselves and their equipment when offering first aid. They will also learn how to sanitise and dress the wound to prevent dirt from entering the wound and causing infection. They will be taught which chemicals are good for sanitisation, and which chemicals are dangerous. -
Protect the wound
Students will learn about antibiotics and medicinal creams or ointments. They will learn about the use of sterile bandages. They will also be taught how to apply the bandage in sustainable ways that prevent wounds from reopening.
Head and Spine Injuries
Head and spine injuries are generally caused by falls, accidents, car crashes and fights. In first aid training you will learn how to care for a patient resourcefully under emergency circumstances. These methods of treatment will involve quick thinking, a knowledge of medical equipment and tools, and a clear ability to classify the severity of the injury. Informed medical classification is the first step to assessing the needs of the patient and determining whether the authorities need to be notified before you can offer on-the-ground support in the meantime.
Types of Head Injuries:
- Headache
- Concussion
- Loss of consciousness
- Nose bleed
- Ear bleed
- Confusion
- Trouble breathing
- Nausea
- Fractured skull
Types of Spine Injuries
Symptoms of Spinal Injury
- Inability to move the limbs or back
- Bone exposure caused by fracture
- Loss of consciousness
- Pressure or stiffness in the back
- Headache or dizziness
- Loss of sensation in extremities
Treating Head and Spine Injuries with First Aid Training
First aid students will learn how to treat victims of head or spinal injuries depending on whether the patient is conscious or not. In most case scenarios, the first aid responder will need to know how to elevate a patient in a neutralised posture and relieve their pressure or pain by attending to any symptoms they have. If the patient is unconscious, the first aid responder will need to know how to keep the patient's airway open so that they do not stop breathing, and how to apply a cervical collar if the neck has been affected.
Choking

Choking is a very common accident that can be life-threatening at times. If you swallow your food incorrectly, or if you swallow any other foreign object, you could potentially block your airway and windpipe, thereby ceasing your breathing. Lack of oxygen to the brain can cause brain damage, so it is vital that choking is stopped immediately. In these cases, first aid training will equip you with the skill to perform emergency tactics that physically dislodge the object or cause.
Symptoms of Choking
- Difficulty breathing
- Heavy, raspy breathing
- Strange, squeaky sounds when breathing
- Coughing
- Skin, hands and lips turning blue or pale
- Flushed face
- Fainting
Treating Choking with First Aid Training Tools
Students will learn how to offer emergency attention to the victim by performing back blows and or abdominal thrusts. Performing back blows generally entails placing one arm around your patient's chest for support and positioning them standing up with their chest facing towards the floor. Thereafter you would deliver 5 blows to the patient's back, in between the shoulders, with the heel of your hand.
Students will also learn how to perform the Heimlich Maneuver, where you deliver 5 abdominal thrusts by standing behind the patient and holding them. This will help the first aid responder to dislodge the object blocking the airway. Students are always encouraged to assess how bad the situation is, and to take the necessary measures by calling medical emergency responders if needed.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and Artificial Respiration
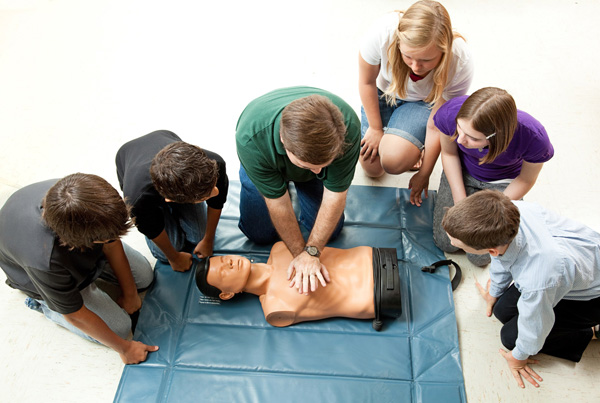
No matter which injury occurs, there is always the chance that a victim might lose consciousness or go into cardiac arrest out of shock. In these cases, the loss of oxygen to the brain is always an extreme concern, as it can cause permanent damage to the brain. To restore blood circulation and breathing, first aid responders will learn how to manually inhibit ventilation with chest compressions in a methodical procedure. These lessons are incredibly valuable, and EMCARE gives all people within first aid training the resources to potentially save a life someday.
GET IN TOUCH
There are a few ways to reach us below. Please feel free to contact us via phone, email or you can send us a message via the form provided and we will get back to you.




















